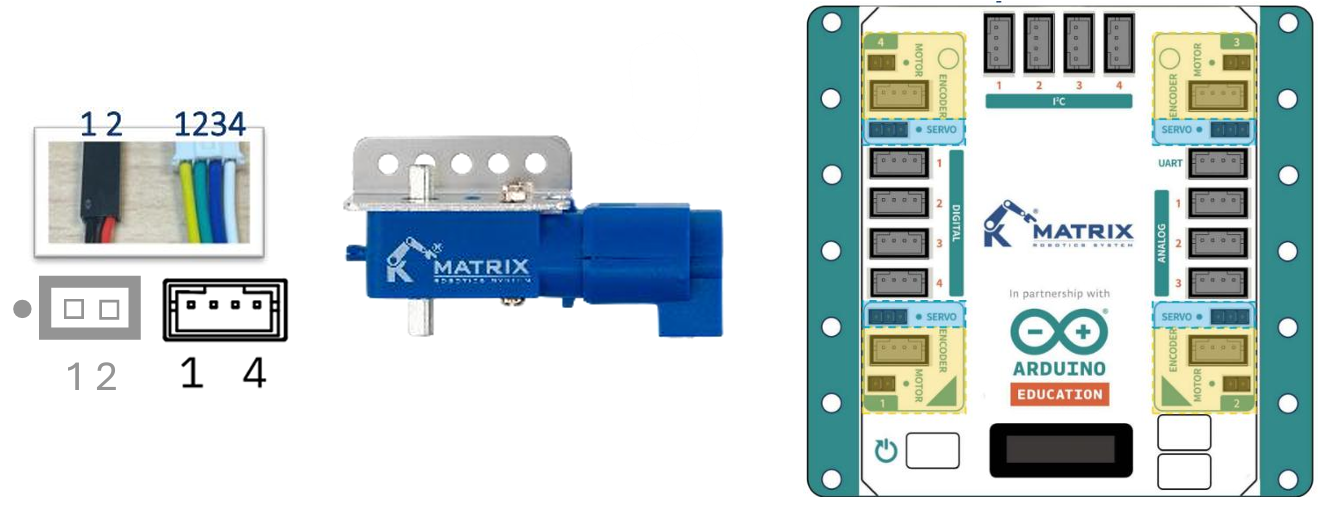
Note: The dot (•) on the motor port indicates the correct side for connecting the ground (GND) wire, which is usually black or sometimes brown in certain motors or servos. Additionally, DC Motors with Encoders require an external battery power source to function properly.
Sample Code
Hardware Connection: Connect the DC Motor with encoder to the M1 port of the MATRIX Mini R4.
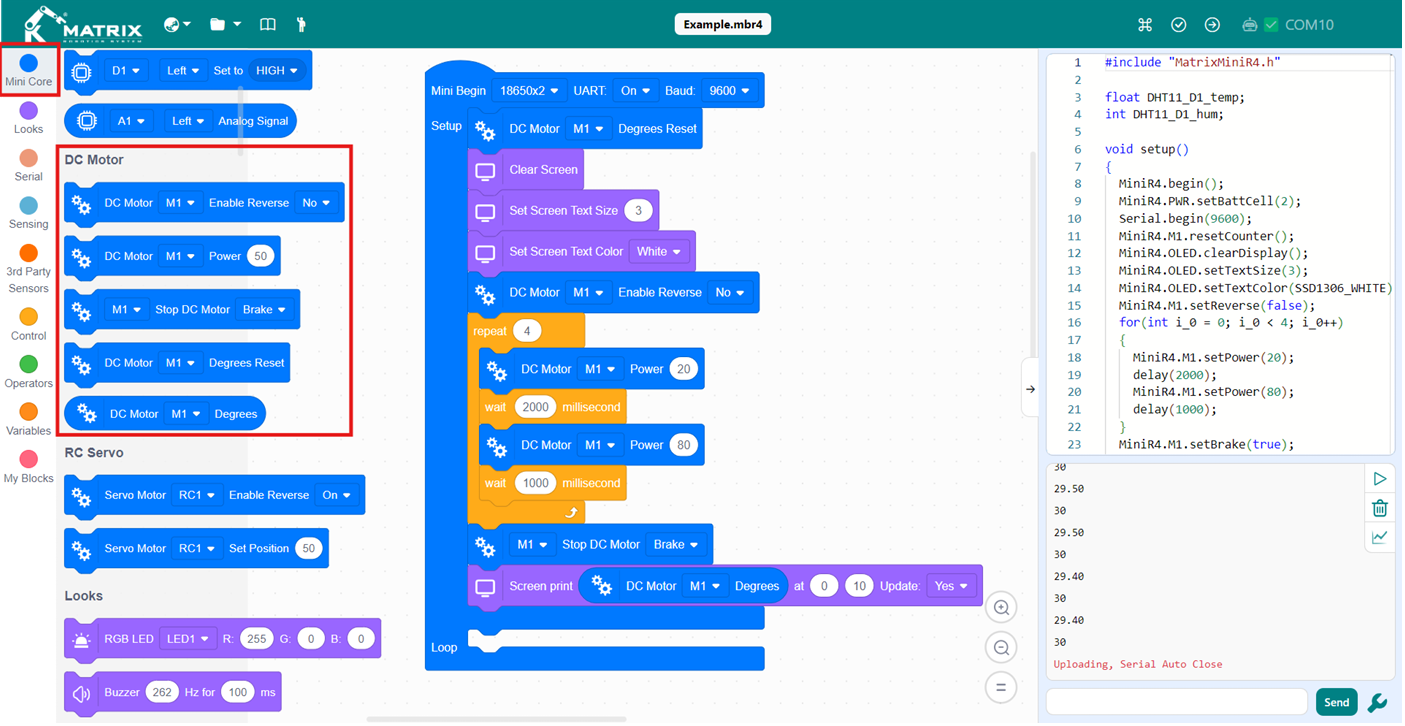
Result: The motor connected to M1 starts to move with 50% of speed. After 2 seconds the motor will move with 80% of speed for 1 second. After 4 times, the motor will be stopped and the degrees of rotation will be shown on the OLED.
Movement Blocks
Note: The movement blocks are optimized for two-wheeled robots and work best with motors equipped with encoders, ensuring accurate and reliable motion control. However, if precise rotation in degrees is not required, you can also synchronize movement using a gyro sensor with non-encoder motors.
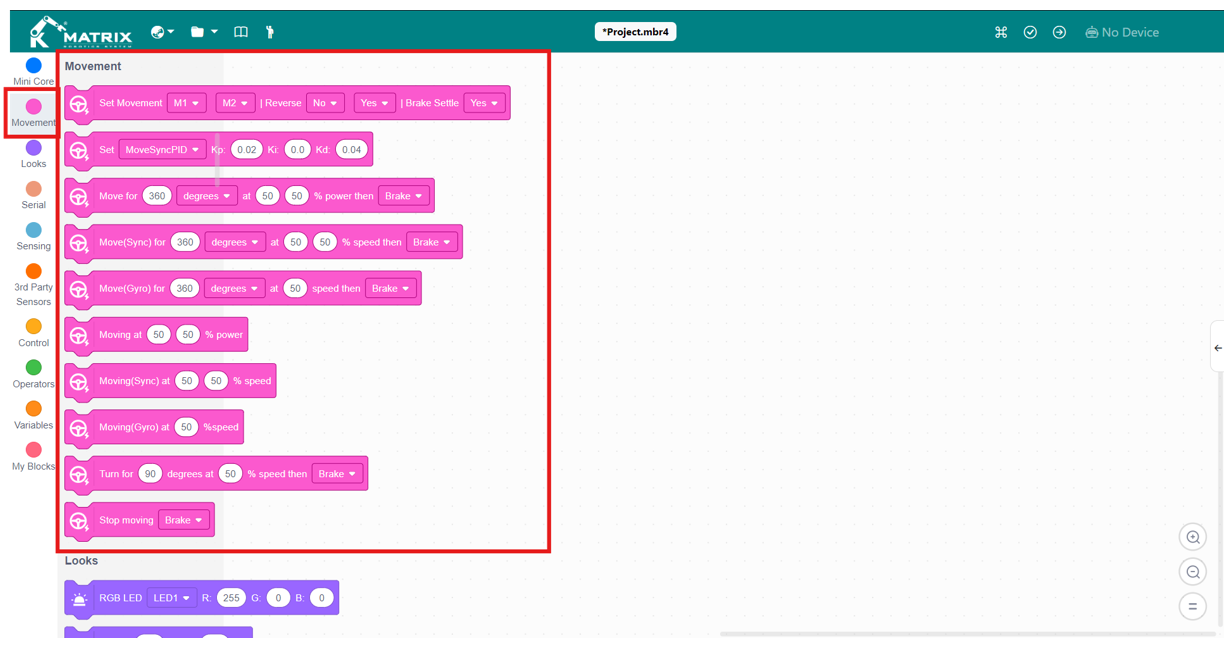
| Block | Instruction |
|---|---|
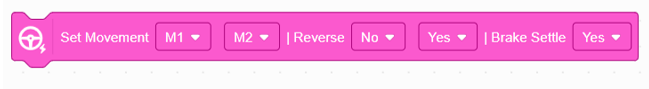 |
This block configures the robot’s drive motors by selecting which motors to use, setting their direction, and enabling or disabling brake settle. It ensures that both motors operate correctly and consistently during movement. |
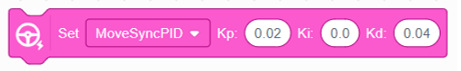 |
This block defines the PID control values (Kp, Ki, Kd) used to keep both motors synced. These values help the robot correct any differences between the motors, resulting in smoother and more straight movement. |
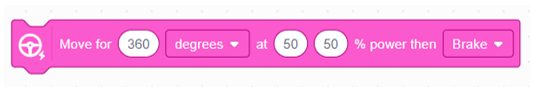 |
This block commands the robot to rotate the motors for a specific number of degrees at a set power level and then apply a brake. It allows controlled movement over a fixed distance. |
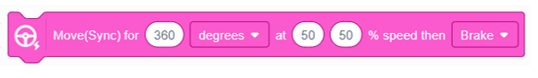 |
This block works like “Move for Degrees” but uses PID control to synchronize both motors. It ensures they move at the same speed, allowing the robot to travel in a straight and accurate line before braking to stop. |
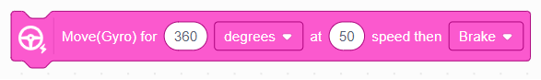 |
This block moves the robot for a specific number of degrees using gyro stabilization. It maintains a straight path by correcting deviations with the gyro sensor, then applies a brake when the movement is complete. |
 |
This block drives the robot continuously at the specified power level for each motor. It does not stop automatically and runs until another command interrupts it. |
 |
This block drives both motors at the same speed with synchronization, helping the robot move in a straight line without using sensors. |
 |
This block drives the robot continuously at the specified speed while using the gyro sensor to keep the heading straight. It runs until another command stops it. |
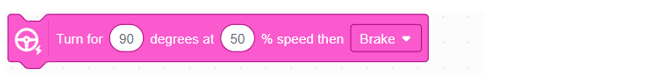 |
This block rotates the robot by a set number of degrees at a chosen speed. After completing the turn, the robot can brake to stop. |
 |
This block immediately stops the robot’s movement. Depending on the setting, it can either brake to stop quickly or coast to a smooth stop. |
